Advanced Dynamic Meshes Course
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
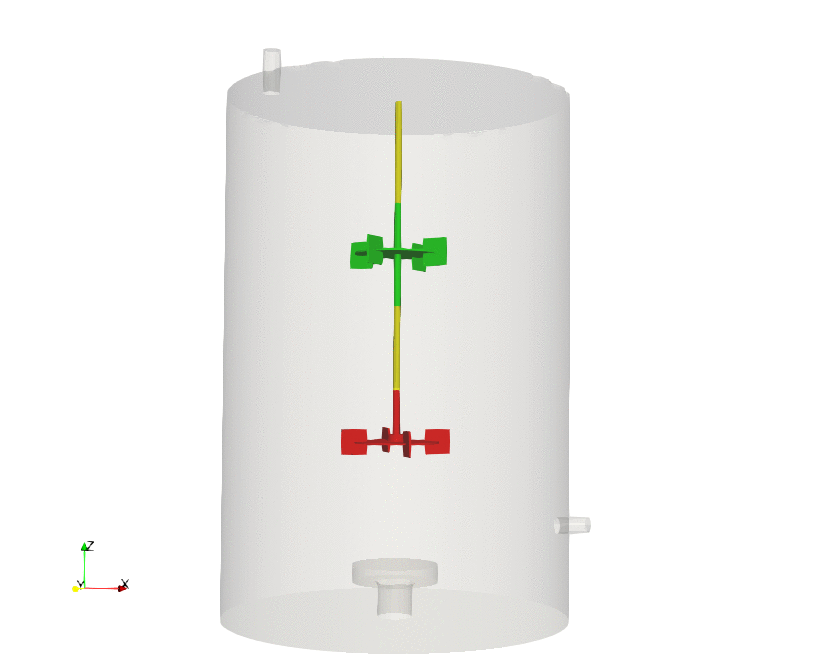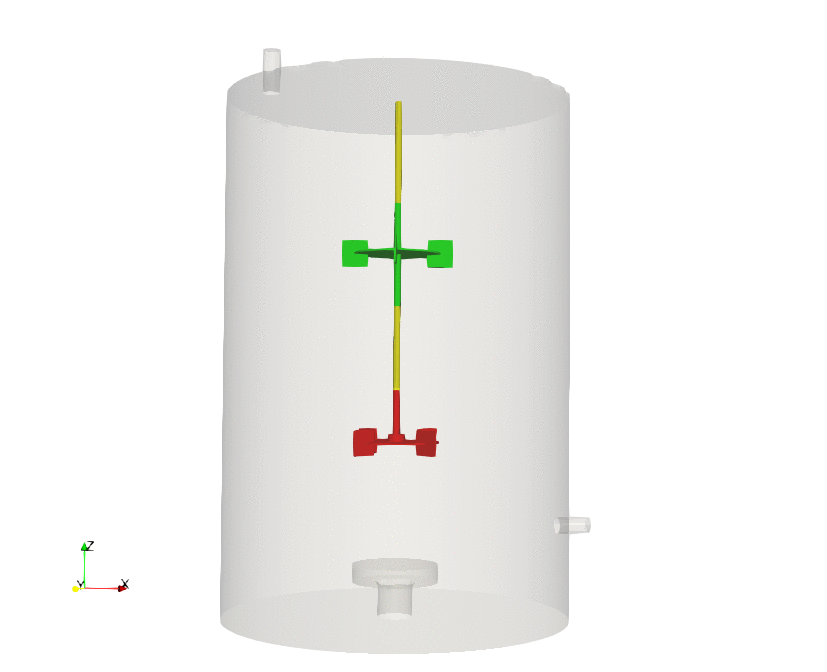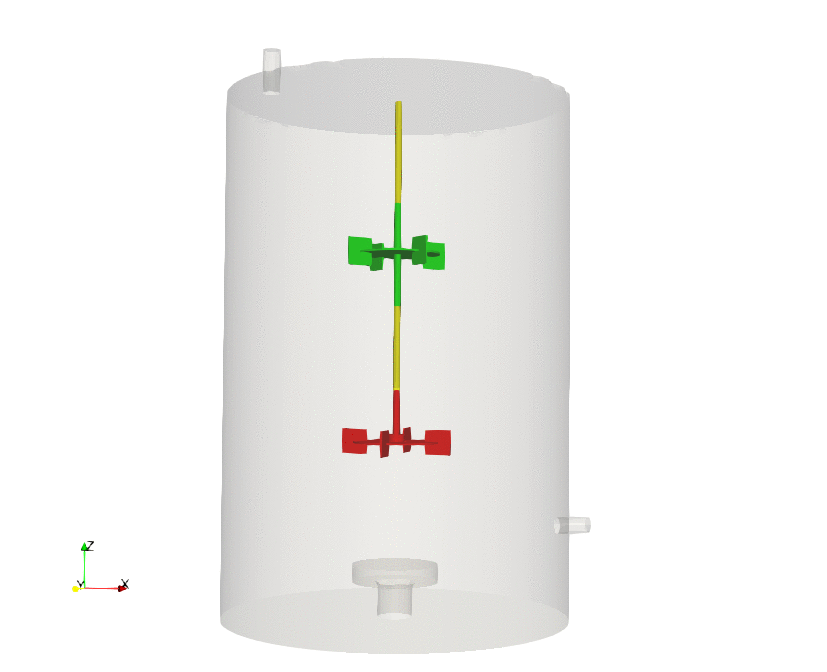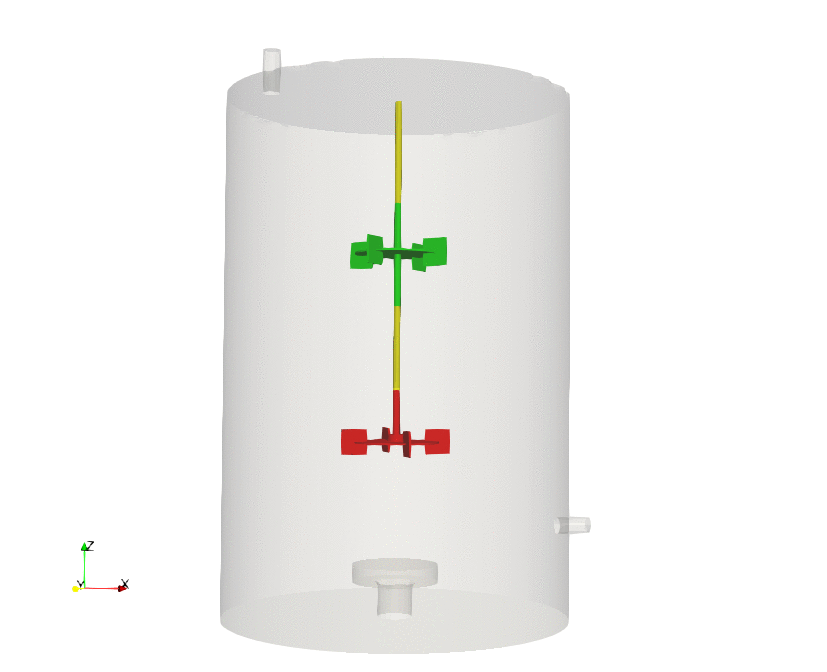
Dynamic meshes are models that allows the mesh to change during a simulation. The changes of the mesh can be due to a prescribed motion, rigid body motion, fluid structure interaction, or refinement/unrefinement of the mesh.
During this course, we address the standard practices to follow when setting dynamic meshes cases in OpenFOAM, and we illustrate the different dynamic meshes approaches implemented in OpenFOAM (morphing meshes, sliding meshes, overset meshes, mesh remeshing and adaptive mesh refinement).
Finally, as dynamic meshes are fully compatible with most of the advanced physical models implemented in OpenFOAM (turbulence, multiphase flows, heat transfer, lagrangian particles), we also illustrate how to setup different physical models and standard best practices.
Topics to be covered:
What are dynamic meshes?
Dynamic meshes in OpenFOAM
Adaptive mesh refinement in OpenFOAM
Sliding meshes in OpenFOAM
Morphing meshes in OpenFOAM
Overset meshes in OpenFOAM
Choosing the right numerics
Advanced post-processing (quantitative and qualitative)
Best practices
Validation cases
For more information, send an email to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Get access to the slides and tutorials at the following link: https://bit.ly/3XOdcww
Disclaimer
Wolf Dynamics makes no warranty, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or usefulness of the information disclosed in this training material. This training material is intended to provide general information only. Any reliance the final user place on this training material is therefore strictly at his/her own risk. Under no circumstances and under no legal theory shall Wolf Dynamics be liable for any loss, damage or injury, arising directly or indirectly from the use or misuse of the information contained in this training material.
